Discuss the different options with your respiratory specialist. Weaning and discontinuation of oxygen therapy.

Oxygen-delivery Devices Chapter 10 Diagram Quizlet
What is a nasal cannula?

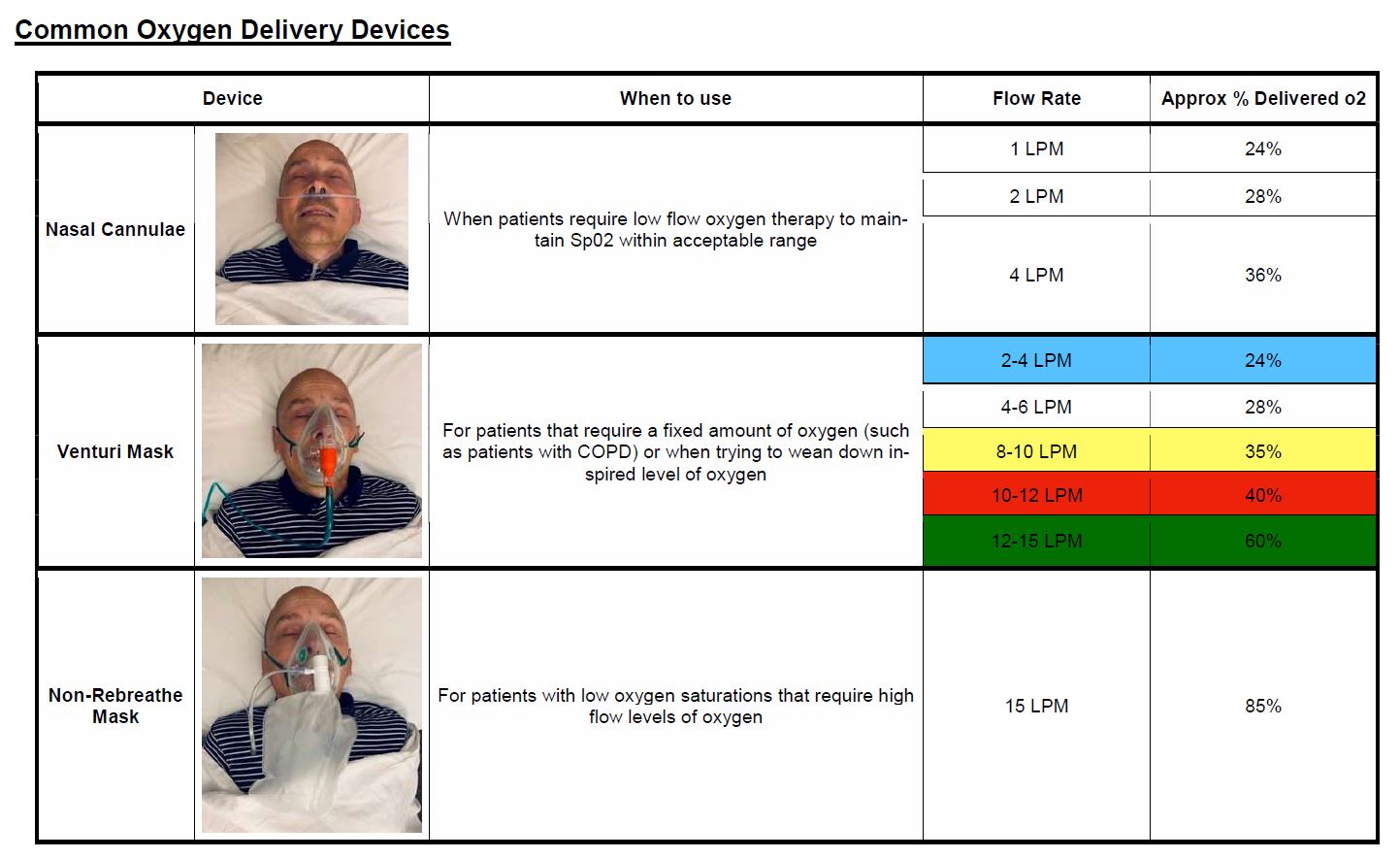
Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates uk. If you need a higher flow rate of oxygen, its likely you will need a face mask. Oxygen should be reduced in. Delivery devices work with different flow rates.
2‐6l/min gives approx 24‐50% fio2. The oxygen flow rate and; Recommended in the guideline as suitable for most pabents with both type i and ii respiratory failure.
Designed to entrain a set amount of o2 and air, which combine to produce a set flow of o2 (the % stated on the venturi). The nasal catheter is a device that is placed. Can be used in patients with stable type ii respiratory failure;
High flow systems show no failure of performance at increased respiratory rates. 2009;6(9):1‐11 bailey p, thomsen ge, spuhler vj, et al.crit care med.jan2007;35(1):139‐145. Below is an image of the fisher and paykel optiflow nasal cannula junior range for.
This table helps doctors choose the right type of. Higher flows (>4 l/min) make it uncomfortable for the patient. There are two important things to consider when delivering supplemental oxygen to your patient:
Per minute will deliver approximately 24 to 44 percent of oxygen to the patient. Fio2 depends on oxygen flow and paent’s minute volume and inspiratory flow and paern of breathing. Figure 11.8 portable oxygen tank.
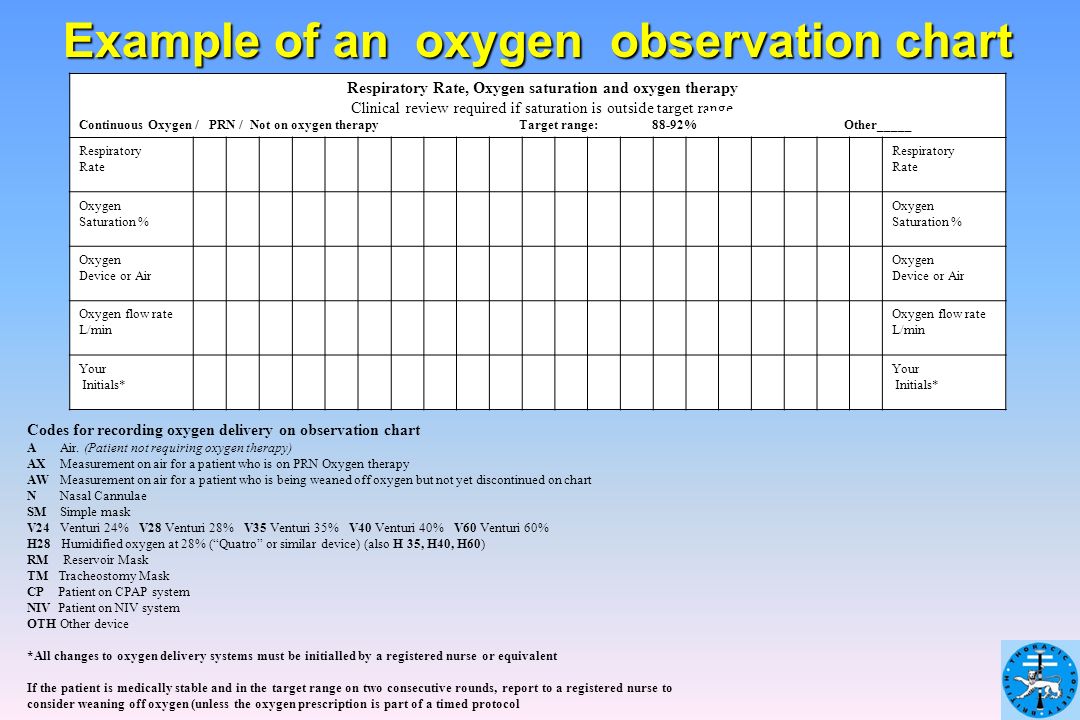
This oxygen delivery devices and flow rates chart shows the o 2 % delivered measured for each tool. Oxygen devices and delivery systems. Oxygen should be prescribed and a signature should be entered on the drug chart on each drug round.
Weaning and discontinuation of oxygen therapy oxygen should be. These low flow oxygen delivery devices are variable performance devices i.e., their performance is effected by changes in patient’s tidal volume and respiratory rate. Very commonly used among the oxygen delivery devices in wards.
Fio 2 (the fraction of inspired oxygen) is defined as the percentage or concentration of oxygen that a person inhales. Prompt clinical assessment is required if oxygen therapy needs to be initiated or increased due to a falling saturation level. 2l = 28%, 3l = 32%, 4l = 36%, 5l = 40%, 6l = 44%.
Oxygen delivery typical flow devices (single use) rate range oxygen sources that can be used with each device. A nasal cannula can be used to deliver up to six litres of oxygen a minute comfortably. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range.
Step up from nasal cannula but doesn’t deliver specific % of oxygen like venturi. Looking at the reliability and variability of oxygen delivery to the patient we can divide these pieces of equipment into fixed performance or variable performance devices. • low flow device • most common device used for mild hypoxia • can be set between 1 and 6 lpm (24% to 40% fio2) • fio2 increases approximately 4% with each liter of o2 korupolur gj, needham dm.contemporary criticalcare.
This means that inspired oxygen concentration is either more dependent on the patient's peak inspiratory flow rate (pifr) ( variable performance devices) or less so ( fixed performance devices). High flow nasal prong therapy (hfnp) see the hfnp nursing clinical guideline for more information. You can breathe in the oxygen from its container either through nasal cannula or a face mask.
Clinical decisions should determine the methods of administration of oxygen therapy and device selection. It is not the l/min stated on the venturi that is delivered to the patient. Dr yusuf imran, j.n.m.c, amu, india
The % of oxygen delivery depends on the flow rate and the delivery device. It is crucial for nurses and transporters to ensure the tank has an adequate amount of oxygen for use during transport, is turned on, and the appropriate flow rate is set. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range.
Oxygen use has extended from inpatient to outpatient settings for patients with chronic pulmonary diseases and complications of hypoxaemia. The flow rate can be set on the wall tap: Oxygen should be signed for on the drug chart on each drug round.
The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device; Fio 2 delivered considerations advantages/ disadvantages can be used with oxygen concentrator compressed oxygen cylinder piped supply oxygen The nasal cannula is a device that has two prongs that are placed in the patient's nostrils and deliver oxygen at flow rates of 1 to 6 liters per minute.

Types Of Oxygen Masks - Slide Share
Equipment For The Inhalation Of Oxygen And Other Gasses Clinical Gate

Abbreviations For Oxygen Devices For Use On Bedside Charts Download Table

Covid-19 And O2 Therapy Initial Prehospital Approach In Mild Symptomatic Patients Medest
Oxygen - Prescribing And Administration In Adults
2
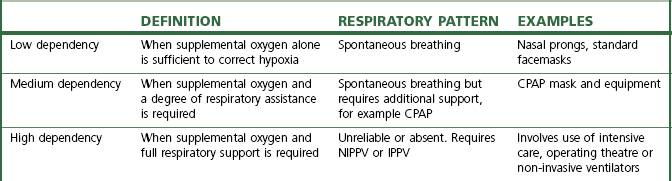
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
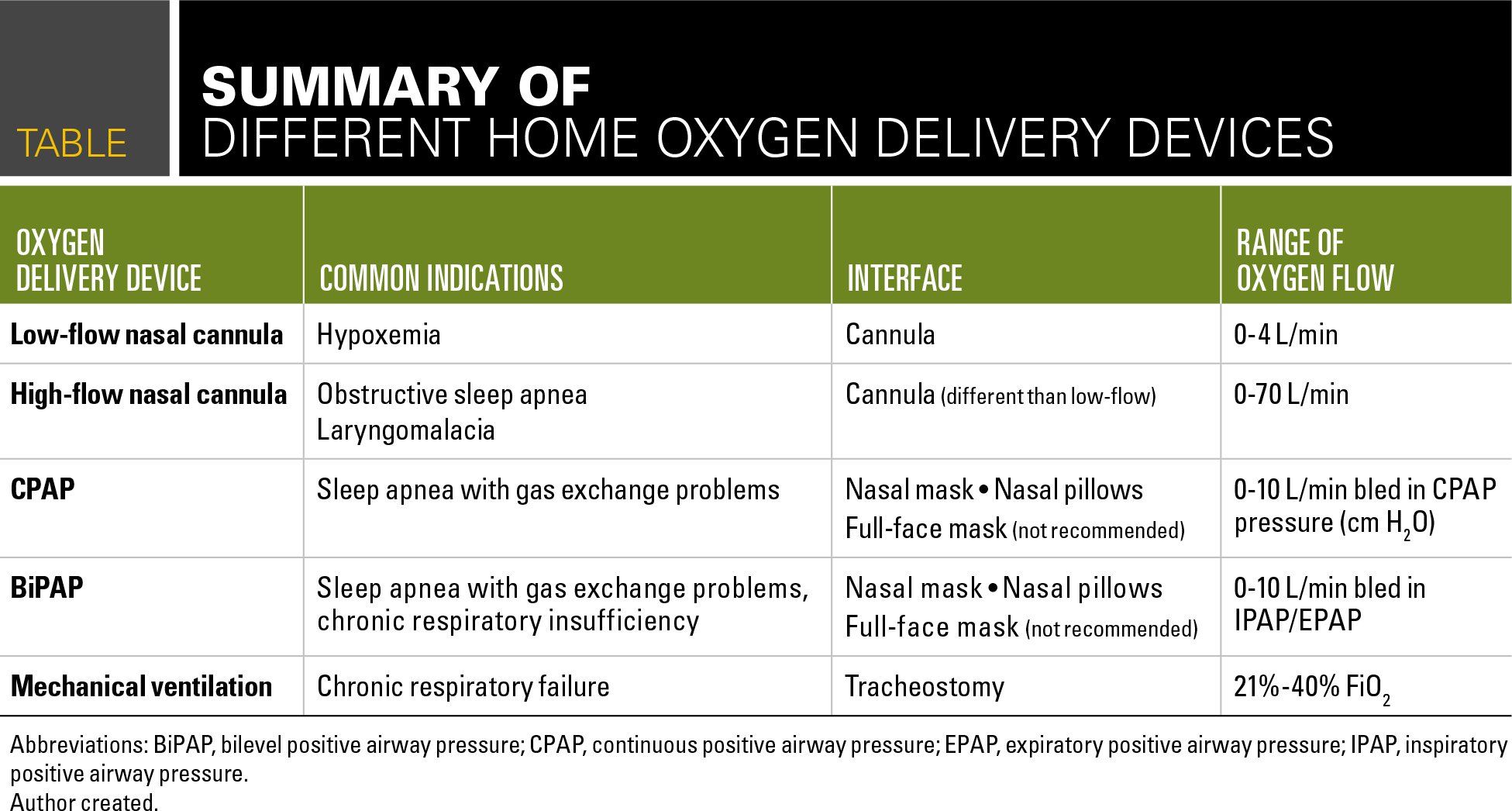
Oxygen Delivery In The Home Setting
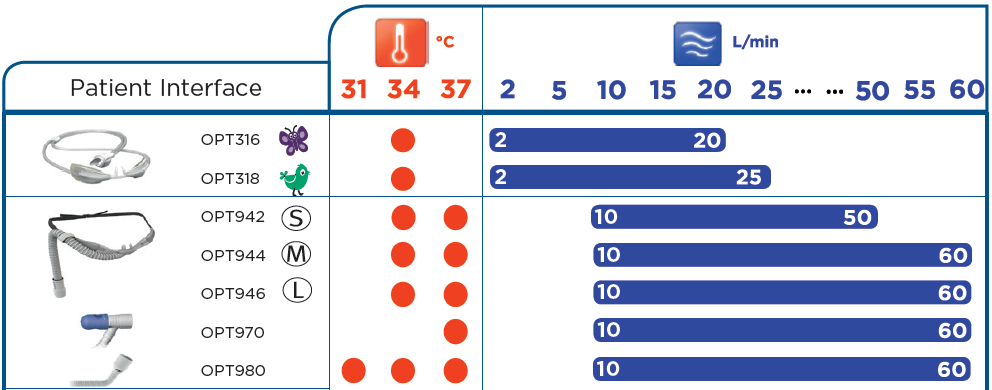
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

British Thoracic Society Guideline For Oxygen Use In
2

Florali The Bottom Line

British Thoracic Society Guideline For Oxygen Use In

British Thoracic Society Guideline For Oxygen Use In

Pin On Fundamentals Of Nursing
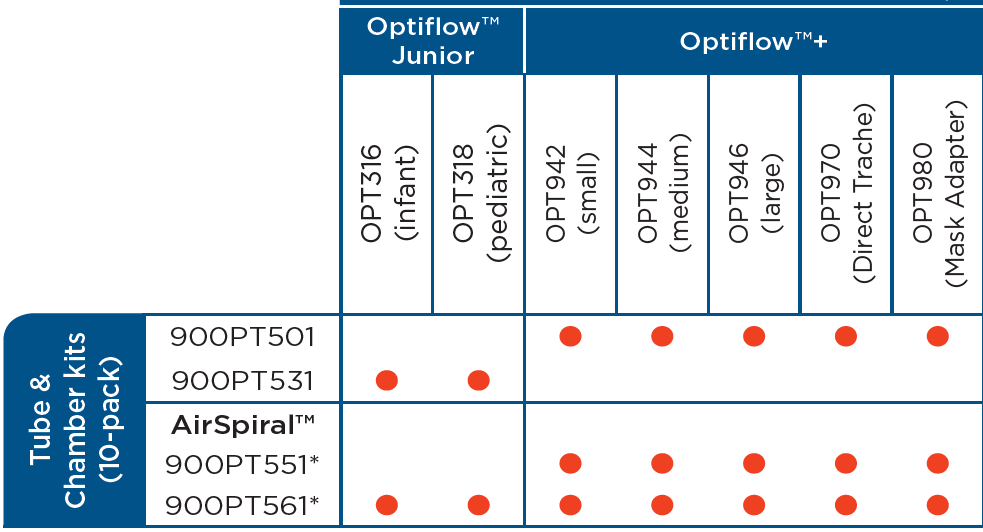
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
Oxygen - Prescribing And Administration In Adults
Medical Gases In Ed - Rcemlearning
Key Messages From The British Thoracic Society Emergency Oxygen Guideline This Presentation Was Last Updated On 0707 Ppt Video Online Download